Modalities in Intraoperative Neuromonitoring:
Neurosurgery
- Somatosensory Evoked Potentials (SSEPs): Measures the integrity of sensory pathways by stimulating peripheral nerves and recording responses at the scalp or spinal cord level.
- Motor Evoked Potentials (MEPs): Assess motor pathway integrity by stimulating the motor cortex and recording muscle responses.
- Electrocorticography (ECoG): Provides continuous monitoring of brain electrical activity, crucial during brain tumor resection or epilepsy surgery.
- Cortical Mapping: Identifies functional areas of the brain to avoid damage during surgery, vital for preserving motor, sensory, and language functions.
Craniotomies (e.g., tumor resection, aneurysm clipping), Deep brain stimulation (DBS) surgeries, Epilepsy surgeries, Skull base surgeries, Functional neurosurgery procedures
Orthopedic Spine Surgery
- Transcranial Electrical Motor Evoked Potentials (tcMEPs): Monitors motor function in the spinal cord and nerve roots, helping prevent paralysis during spine surgeries.
- SSEPs: Ensures spinal cord integrity and helps identify potential ischemia during complex spinal procedures.
- Electromyography (EMG): Records electrical activity from muscles to locate and protect nerves, particularly during decompressions and fusions.
Spinal fusions (e.g., cervical, thoracic, lumbar), Scoliosis corrections, Spine tumor resections, Disc herniation surgeries, Spinal deformity corrections
Vascular Surgery
- SSEPs: Monitors spinal cord function during aortic aneurysm repairs to prevent spinal cord injury.
- MEPs: Ensures motor function preservation during complex vascular procedures involving the spine.
- Peripheral Nerve Monitoring: Protects peripheral nerves during surgeries involving vascular structures close to nerve pathways.
Aortic aneurysm repairs (open and endovascular), Carotid endarterectomy (CEA), Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) repairs, Microvascular decompression (MVD), Complex vascular reconstructions
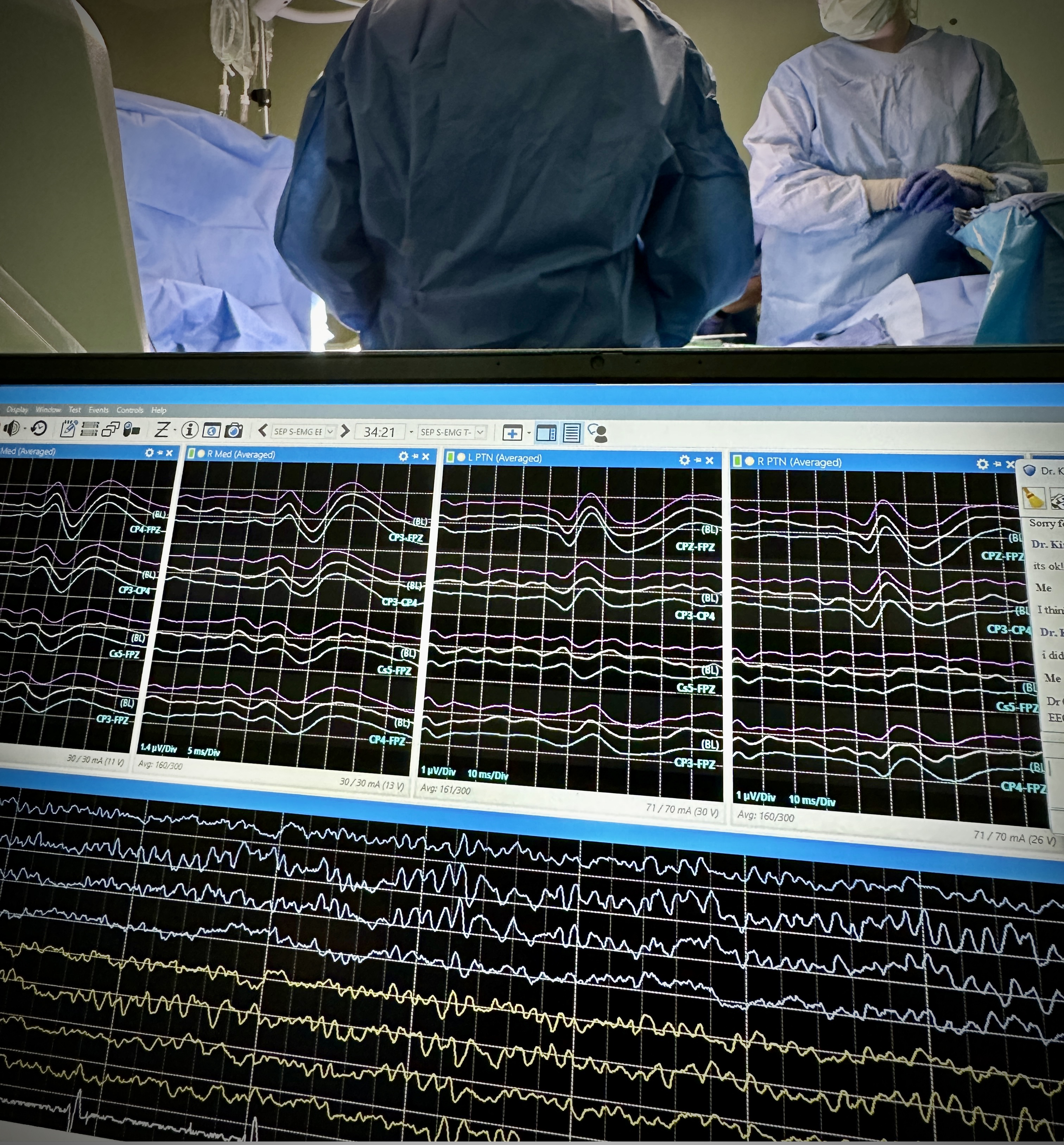
In all of these surgeries, intraoperative neuromonitoring serves as a critical adjunct to the surgical team, providing real-time feedback on neurological function. This enables surgeons to make informed decisions, adjust surgical techniques, and potentially prevent neurological complications that could impact patient outcomes. Each modality and application is tailored to the specific surgical context, ensuring comprehensive monitoring and patient safety throughout the procedure.
